- What is Financial Modeling?
- Key Principles and Concepts of Financial Modeling
- Types of Financial Models
- Financial Modeling Examples for Various Industries
- Best Practices for Effective Financial Modeling
- Tools and Software for Financial Modeling
- Challenges and Common Mistakes in Financial Modeling
- Advanced Techniques in Financial Modeling
- Ethical Considerations in Financial Modeling
- Career Opportunities in Financial Modeling
- Conclusion
Making informed decisions is crucial for business success. This guide equips you with industry-specific financial modeling examples, best practices, and advanced techniques to navigate the complexities of financial modeling. Explore the world of financial modeling and empower yourself to drive financial success.
What is Financial Modeling?
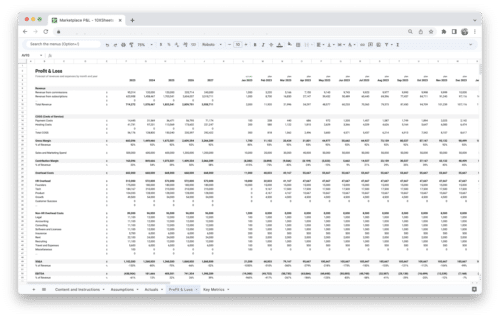
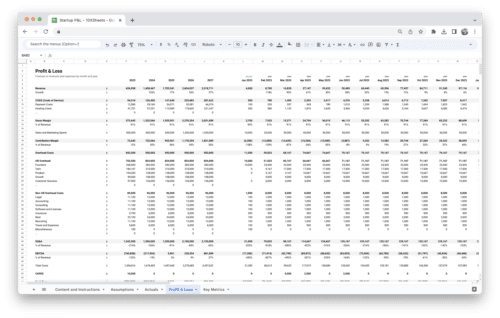
Financial modeling is the process of creating a mathematical representation of a real-world financial situation or scenario. It involves building mathematical models and using them to analyze and forecast financial outcomes. The purpose of financial modeling is to support decision-making, assess the financial feasibility of projects, value assets or companies, and guide strategic planning.
Importance of Financial Modeling in Decision-Making
Financial modeling plays a crucial role in decision-making processes across various industries. By incorporating relevant financial data and assumptions, models provide a structured framework for evaluating potential outcomes and risks. Financial models help make informed decisions regarding investment opportunities, budgeting, pricing strategies, capital allocation, and more.
Benefits of Using Financial Models
Financial models offer several benefits to organizations and individuals:
- Improved Decision-Making: Financial models provide a systematic approach to assess the financial impact of different scenarios, enabling decision-makers to choose the best course of action.
- Risk Assessment: Models facilitate sensitivity and scenario analyses, helping identify and quantify potential risks and their impact on financial outcomes.
- Forecasting Accuracy: By using historical data and future projections, financial models assist in generating accurate forecasts for revenue, expenses, and cash flows.
- Communication and Stakeholder Engagement: Models serve as a visual representation of financial data, making it easier to communicate complex concepts and engage stakeholders in discussions.
- Performance Evaluation: Financial models help track and compare actual results against forecasts, enabling performance evaluation and strategic adjustments.
Key Principles and Concepts of Financial Modeling
To build effective financial models, it is essential to understand fundamental principles and concepts that underpin financial analysis. Let’s delve into some basic concepts that form the foundation of financial modeling.
Time Value of Money
The time value of money principle recognizes that the value of money changes over time due to factors such as inflation and the opportunity cost of investing or borrowing funds. Key concepts associated with the time value of money include:
- Present Value (PV): The current value of future cash flows, obtained by discounting them at an appropriate interest rate.
- Future Value (FV): The value of an investment or cash flow at a future point in time, accounting for compounding.
Cash Flow Projection
Cash flow projection involves estimating the future inflows and outflows of cash for a business or investment. It helps understand the timing and magnitude of cash flows, assisting in financial planning and decision-making. Essential elements of cash flow projection include:
- Operating Cash Flows: Cash generated from day-to-day business operations.
- Investing Cash Flows: Cash flows related to capital expenditures and investments.
- Financing Cash Flows: Cash flows associated with raising or repaying capital, such as issuing debt or equity.
Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) Analysis
DCF analysis is a valuation method used to determine the present value of future cash flows. It involves discounting projected cash flows using an appropriate discount rate, such as the weighted average cost of capital (WACC). DCF analysis helps in assessing the intrinsic value of an investment or company.
Financial Statements Analysis
Financial statements analysis involves the examination of a company’s financial statements, such as the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement. It helps in understanding a company’s financial performance, profitability, liquidity, and solvency. Key ratios and metrics used in financial statements analysis include:
- Profitability Ratios: Gross profit margin, operating margin, net profit margin.
- Liquidity Ratios: Current ratio, quick ratio, cash ratio.
- Solvency Ratios: Debt-to-equity ratio, interest coverage ratio, debt ratio.
- Efficiency Ratios: Inventory turnover ratio, receivables turnover ratio, asset turnover ratio.
Sensitivity Analysis
Sensitivity analysis involves assessing the impact of changes in key variables or assumptions on the financial model’s outputs. By conducting sensitivity analysis, analysts can identify the most critical drivers of financial performance and evaluate the model’s robustness to different scenarios.
Scenario Analysis
Scenario analysis extends sensitivity analysis by examining the financial outcomes under multiple plausible scenarios. Analysts create various scenarios by adjusting different assumptions to understand the potential range of outcomes and associated risks.
Types of Financial Models
Financial modeling encompasses various types of models tailored to specific purposes.
Forecasting Models
Forecasting models are used to predict future financial performance based on historical data and projected trends. Some standard forecasting models include:
- Revenue Forecasting Model: Projects future revenue based on sales volume, pricing, market growth, and other factors.
- Expense Forecasting Model: Estimates future expenses, including operating costs, salaries, marketing expenses, and more.
- Budgeting Model: A comprehensive financial model incorporating revenue and expense forecasts to create a budget for a specific period.
Valuation Models
Valuation models are utilized to determine the value of assets, companies, or investment opportunities. Here are some widely used valuation models:
- Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) Model: Estimates the present value of expected cash flows to determine the intrinsic value of an investment or company.
- Comparable Company Analysis Model: Compares the financial metrics of a target company to those of similar publicly traded companies to assess its relative value.
- Precedent Transactions Analysis Model: Examines past mergers and acquisitions transactions in the industry to evaluate the potential value of a target company.
Capital Structure Models
Capital structure models focus on analyzing the composition of a company’s capital, including debt and equity. Examples of capital structure models include:
- Debt Schedule Model: Tracks the details of a company’s debt, including interest rates, maturities, and repayment schedules.
- Equity Dilution Model: Calculates the impact of issuing new shares on the ownership percentage and value of existing shareholders.
Mergers and Acquisitions (M&A) Models
M&A models are used to evaluate the financial implications of mergers, acquisitions, or other strategic transactions. Some common M&A models include:
- Merger Model: Assesses the financial impact of combining two companies through a merger.
- Accretion/Dilution Model: Determines how a proposed acquisition would impact the acquirer’s earnings per share (EPS).
- LBO (Leveraged Buyout) Model: Evaluates the financial feasibility of acquiring a company using significant debt.
Financial Modeling Examples for Various Industries
Financial modeling finds applications across different industries.
Technology Industry
The technology industry often requires financial models to assess investment opportunities and support strategic decisions. Some examples of financial models in the technology industry include:
- Software as a Service (SaaS) Company Financial Model: This model forecasts revenue based on subscription pricing, customer acquisition rates, churn rates, and other factors specific to the SaaS business model.
- E-commerce Startup Financial Model: This model incorporates sales projections, marketing expenses, customer acquisition costs, and fulfillment costs to assess the financial viability of an e-commerce startup.
Manufacturing Industry
In the manufacturing industry, financial models help evaluate capital investments, cost analysis, and production planning. Here are two financial modeling examples for the manufacturing industry:
- Manufacturing Plant Expansion Financial Model: This model assesses the financial feasibility of expanding an existing manufacturing plant. It considers factors such as the cost of acquiring new machinery, construction expenses, labor costs, anticipated increase in production capacity, and projected revenue growth. The model incorporates cash flow projections, investment analysis, and sensitivity analysis to determine the viability and potential return on investment of the expansion project.
- Equipment Replacement Financial Model: In manufacturing, evaluating the optimal time for replacing equipment is crucial to maximize operational efficiency and minimize costs. This financial model helps determine the financial impact of replacing equipment by considering factors such as the cost of new equipment, expected savings in maintenance and energy costs, potential increase in production output, and the impact on cash flows over the equipment’s useful life. The model allows for scenario analysis to compare different replacement options and determine the most cost-effective solution.
Real Estate Industry
Financial modeling is widely used in the real estate industry for investment analysis, property valuation, and development projects. Financial modeling examples in the real estate industry include:
- Real Estate Development Financial Model: This model is used to evaluate the financial feasibility of a real estate development project. It incorporates projected construction costs, land acquisition expenses, anticipated rental or sales revenue, operating expenses, financing costs, and expected market conditions. The model calculates vital financial metrics such as net present value (NPV), internal rate of return (IRR), and return on investment (ROI) to determine the viability and profitability of the development project.
- Rental Property Investment Financial Model: This model is used by investors to assess the financial performance of rental properties. It considers factors such as property purchase price, rental income, operating expenses, financing costs, vacancy rates, and potential appreciation. The model helps calculate key metrics such as cash-on-cash return, cap rate, and net operating income (NOI) to evaluate rental properties’ investment potential and profitability.
Financial Services Industry
Financial modeling is essential for portfolio analysis, risk management, and investment decision-making in the financial services industry. Some financial modeling examples for the financial services industry include:
- Investment Portfolio Analysis Model: This model helps analyze the performance and risk of investment portfolios. It incorporates data on asset allocation, individual asset performance, market indicators, and risk measures. The model allows for scenario analysis, stress testing, and sensitivity analysis to evaluate the potential impact of market fluctuations on the portfolio’s returns and risk profile. It aids in optimizing asset allocation and making informed investment decisions.
- Risk Management Model: Risk management models are used to assess and mitigate financial risks in the financial services industry. These models incorporate historical data, market indicators, and risk metrics to quantify potential risks and estimate the impact on financial outcomes. They help identify vulnerability areas, implement risk mitigation strategies, and determine optimal capital reserves to safeguard against unexpected events.
Best Practices for Effective Financial Modeling
To ensure the accuracy, reliability, and usability of financial models, it is essential to follow best practices. Incorporating these practices enhances the quality of the models and improves decision-making processes. Let’s explore some critical best practices for effective financial modeling:
1. Assumption Sensitivity and Error Checking
- Validate and verify assumptions by cross-referencing with reliable data sources.
- Conduct sensitivity analysis to understand the impact of varying assumptions on financial outcomes.
- Implement error checks and validation rules to identify and correct data input errors.
2. Proper Formatting and Organization
- Use consistent formatting, clear labels, and logical structure to enhance model readability.
- Group related inputs and outputs together to improve model organization and ease of navigation.
- Utilize color coding and cell formatting to highlight important outputs, key assumptions, and formulas for easy identification.
3. Consistency and Accuracy in Formulas
- Ensure that formulas are consistent and error-free throughout the model.
- Avoid hardcoding values and instead utilize cell references to improve flexibility and ease of updates.
- Regularly review and validate formulas to maintain accuracy.
4. Use of Clear and Understandable Labels
- Use descriptive and intuitive labels for cells, inputs, and outputs.
- Include units of measurement to avoid confusion.
- Provide clear explanations or comments for complex formulas or calculations.
5. Sensible Use of Macros and Automation
- Leverage macros and automation to streamline repetitive tasks and reduce manual errors.
- Use caution when implementing macros, ensuring they are well-documented and thoroughly tested.
6. Regular Model Updating and Reviewing
- Update the model regularly with the latest data and assumptions.
- Perform periodic reviews to identify any errors, inconsistencies, or outdated information.
- Maintain documentation to track changes and provide transparency.
Tools and Software for Financial Modeling
Financial modeling can be performed using various tools and software that offer different features and functionalities, including spreadsheet tools, financial modeling software, and online platforms.
The most popular tools for financial modeling are:
- Microsoft Excel: Widely used for financial modeling due to its versatility and extensive formula capabilities.
- Google Sheets: Offers collaborative features and cloud-based accessibility for team collaboration.
Challenges and Common Mistakes in Financial Modeling
While financial modeling is a powerful tool, it comes with challenges and potential pitfalls. Being aware of these challenges helps avoid common mistakes and improves the accuracy and reliability of financial models. Let’s explore some challenges and common errors in financial modeling:
1. Overreliance on Assumptions
- Uncertain assumptions can significantly impact model outputs, so it’s crucial to validate assumptions with data and expert insights.
- Sensitivity analysis can help assess the sensitivity of the model to different assumptions.
2. Ignoring Risks and Uncertainties
- Failing to incorporate potential risks and uncertainties can lead to overly optimistic projections.
- Conduct thorough risk assessments and consider various scenarios to account for potential risks and their impact on financial outcomes.
3. Inadequate Sensitivity Analysis
- Lack of comprehensive sensitivity analysis limits understanding of the model’s sensitivity to changes in key variables.
- Perform sensitivity analysis across multiple variables to assess their impact on financial outputs.
4. Lack of Documentation and Version Control
- Inadequate documentation makes it difficult to understand and review the model.
- Maintain proper documentation of assumptions, data sources, formulas, and key changes made to the model.
- Implement version control to track model iterations and updates.
Advanced Techniques in Financial Modeling
To further enhance the sophistication and accuracy of financial models, advanced techniques can be employed. These techniques go beyond basic modeling principles and incorporate additional tools and methodologies. Here are some advanced techniques in financial modeling:
Monte Carlo Simulation
- Monte Carlo simulation involves generating multiple random scenarios based on probability distributions of key variables.
- It helps assess the range of possible outcomes and understand the probability of achieving specific financial targets.
Decision Tree Analysis
- Decision tree analysis visualizes decisions and potential outcomes in a tree-like structure.
- It helps evaluate the financial impact of different decision paths and the optimal course of action.
Optimization Models
- Optimization models use mathematical algorithms to identify the best combination of inputs to maximize desired outputs or minimize costs.
- These models are useful for resource allocation, portfolio optimization, and production planning.
Advanced Sensitivity Analysis
- Advanced sensitivity analysis techniques, such as tornado diagrams and spider charts, provide a visual representation of the sensitivity of outputs to different inputs.
- They help identify the most influential factors and prioritize risk mitigation strategies.
Ethical Considerations in Financial Modeling
Ethics play a crucial role in financial modeling to ensure transparency, accuracy, and responsible decision-making. Here are some ethical considerations to keep in mind:
Transparency and Accuracy
- Provide clear documentation and explanations for all assumptions, data sources, and calculations used in the model.
- Avoid manipulating data or using biased assumptions to create a desired outcome.
Assumptions and Biases
- Recognize and disclose any potential biases in assumptions or data sources that may impact the objectivity of the model.
- Strive for unbiased and objective analysis to ensure accurate decision-making.
Data Privacy and Security
- Adhere to data privacy regulations and protect sensitive information used in financial modeling.
- Implement appropriate security measures to safeguard data against unauthorized access or breaches.
Career Opportunities in Financial Modeling
Financial modeling skills are highly valued in various industries, offering rewarding career opportunities. Here are some aspects to consider when exploring a career in financial modeling:
Roles and Responsibilities
- Financial Analyst: Prepare financial models, conduct analysis, and provide insights for decision-making.
- Investment Banker: Build complex financial models for valuations, mergers, and acquisitions.
- Financial Consultant: Develop customized financial models for clients and provide strategic advice.
Required Skills and Qualifications
- Strong analytical and quantitative skills.
- Proficiency in financial modeling techniques and software.
- Knowledge of finance, accounting, and industry-specific factors.
Industry Trends and Job Market Outlook
- Increasing demand for financial modeling expertise due to the growing complexity of financial decisions.
- Job prospects are favorable in investment banking, consulting, private equity, and corporate finance sectors.
Conclusion
Financial modeling is a valuable tool that supports decision-making, improves forecasting accuracy, and enhances financial analysis. By understanding the fundamental principles, using best practices, and exploring industry-specific financial modeling examples, you can build effective financial models for various purposes. Remember to stay up-to-date with advanced techniques, ethical considerations, and the evolving job market to excel in the field of financial modeling. Continuous learning and practice are essential to refine your skills and make informed financial decisions in today’s dynamic business environment.
Get Started With a Prebuilt Template!
Looking to streamline your business financial modeling process with a prebuilt customizable template? Say goodbye to the hassle of building a financial model from scratch and get started right away with one of our premium templates.
- Save time with no need to create a financial model from scratch.
- Reduce errors with prebuilt formulas and calculations.
- Customize to your needs by adding/deleting sections and adjusting formulas.
- Automatically calculate key metrics for valuable insights.
- Make informed decisions about your strategy and goals with a clear picture of your business performance and financial health.