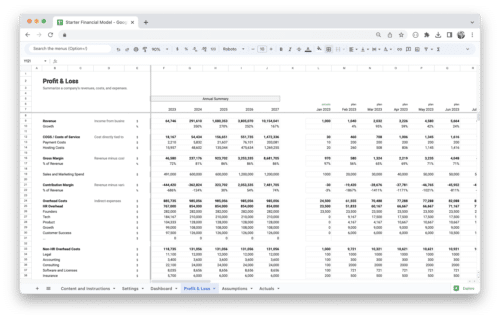
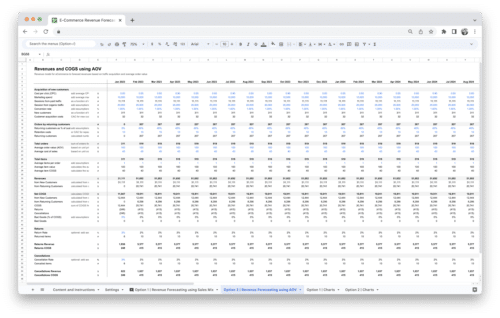
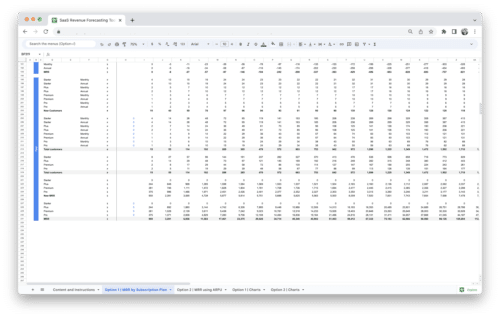
Have you ever wondered how successful businesses gauge their profitability and make strategic financial decisions? In the world of commerce, one vital metric stands out as a compass for financial health and growth: gross profit. In this guide, we’ll unravel the intricacies of gross profit, explore its significance in the business landscape, and equip you with the knowledge and tools to navigate the complex terrain of financial management. Whether you’re a seasoned entrepreneur or just starting your venture, understanding gross profit is essential for steering your business toward financial prosperity.
What Is Gross Profit?
Gross profit is a financial metric that represents the profit a company generates from its core business operations. It is calculated by subtracting the direct costs associated with producing or acquiring the goods or services your business sells from its total revenue.
Gross profit excludes various expenses, such as operating expenses, interest, taxes, and non-operating costs. Instead, it focuses solely on the direct costs directly linked to the production or acquisition of your products or services.
Importance of Gross Profit
Gross profit plays a pivotal role in your business for several reasons:
- Profitability Assessment: Gross profit is a primary indicator of how profitable your core business operations are. It allows you to evaluate the success of your primary revenue-generating activities.
- Cost Management: By examining gross profit, you can pinpoint areas where cost management and optimization are possible. This insight helps identify opportunities to increase profit margins.
- Pricing Strategies: Gross profit analysis aids in the formulation of pricing strategies. It enables you to set prices that not only cover your production costs but also provide room for profit.
- Investor and Lender Confidence: Investors and lenders often scrutinize gross profit to assess a business’s financial health. A healthy gross profit margin can instill confidence and attract investment or lending opportunities.
- Performance Tracking: Regularly monitoring gross profit allows you to track your business’s financial performance over time. It helps you identify trends and make informed decisions to enhance profitability.
In summary, gross profit is a fundamental financial metric that measures the profitability of your core business activities. Its importance lies in its ability to guide pricing strategies, cost management, and overall financial health, making it a vital tool for successful business management.
Why Gross Profit Matters in Business
Gross profit matters in business for a variety of reasons, all of which contribute to the overall success and sustainability of your company. Let’s explore the significance of gross profit in greater detail:
Pricing Strategies
Gross profit is closely tied to your pricing strategies. It provides insights into how much revenue you retain after covering the direct costs of production or acquisition. Understanding your gross profit margin helps you set prices that are not only competitive but also profitable. Balancing competitive pricing with healthy profit margins is essential for long-term success.
Cost Control
Effective cost control is a key driver of gross profit improvement. By analyzing your gross profit, you can identify areas where production or acquisition costs can be reduced. This may involve renegotiating supplier contracts, optimizing manufacturing processes, or implementing cost-saving measures. Lowering your Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) can directly impact your gross profit margin.
Financial Decision-Making
Gross profit plays a crucial role in financial decision-making. It helps you assess the feasibility of new projects, expansion plans, or product launches. Additionally, it serves as a foundation for other financial metrics, such as net profit and EBITDA (Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization), which are essential for strategic planning and investment considerations.
Investor Confidence
Investors and stakeholders closely examine gross profit when evaluating a company’s financial health and potential for growth. A healthy gross profit margin signals efficient cost management and profitability, which can attract investors and contribute to your company’s overall valuation.
Performance Evaluation
Regularly tracking and analyzing gross profit allows you to evaluate your business’s performance over time. It provides a historical perspective on your profitability trends, helping you identify areas of strength and weakness. This information empowers you to make data-driven decisions to enhance your business’s financial performance.
Gross profit matters in business because it serves as a critical indicator of profitability, guides pricing strategies, informs cost control measures, and influences investor confidence. It is a cornerstone metric that underpins your financial decision-making and overall success as a business owner or manager.
How to Calculate Gross Profit?
Gross profit is a crucial financial metric that provides insights into your business’s profitability. In this section, we’ll explore the key components of calculating gross profit in more detail.
Gross Profit Formula
To calculate gross profit, you’ll use a straightforward formula:
Gross Profit = Revenue – Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
This formula represents the foundation of understanding how much money your business generates after covering the direct costs associated with producing or acquiring the goods and services you sell. Let’s delve deeper into each component.
Understanding Revenue
Revenue, often referred to as sales or turnover, forms the starting point of your gross profit calculation. It encompasses the total income generated from selling your products or services. However, it’s essential to distinguish between gross revenue and net revenue to gain a comprehensive understanding.
Gross revenue represents the total amount before any deductions, such as discounts or returns. Net revenue, on the other hand, reflects the revenue after accounting for these deductions, providing a more accurate picture of your business’s financial performance.
How to Determine Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)?
The Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) represents all direct costs associated with the production or acquisition of the goods and services your business offers. These costs typically encompass:
- Raw Materials: The expenses related to the materials required for manufacturing your products.
- Labor: Costs associated with the workforce directly involved in production.
- Manufacturing or Production Costs: Overheads, equipment maintenance, and utilities relevant to the production process.
Precisely determining your COGS is critical for an accurate gross profit calculation. By breaking down these costs, you can gain insights into the areas where cost management and optimization are possible.
How to Calculate Gross Profit?
Calculating gross profit involves a straightforward step-by-step process:
- Start with your total revenue: This should include all income generated from selling your products or services.
- Subtract the cost of goods sold (COGS): This includes all direct costs associated with the production or acquisition of your goods.
- The result is your gross profit: It represents the amount of money your business retains after covering the costs directly tied to producing or acquiring the products or services.
By following these steps and understanding the components involved, you’ll have a clear picture of your business’s gross profit, a critical metric for assessing profitability and making informed financial decisions.
Gross Profit Margin
Gross profit margin is a key financial metric that offers valuable insights into the profitability and efficiency of your business operations.
What Is Gross Profit Margin?
Gross profit margin is a percentage that indicates the proportion of your revenue that remains as gross profit after accounting for the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS). In essence, it quantifies how effectively your business manages its production or acquisition costs relative to its total revenue.
Gross Profit Margin = (Gross Profit / Revenue) x 100
Understanding and calculating this metric is essential because it provides a clear picture of how efficiently your business converts revenue into profit. A higher gross profit margin generally indicates better cost management and profitability.
How to Calculate Gross Profit Margin?
To calculate gross profit margin, you can use the formula mentioned above. First, determine your gross profit by subtracting your COGS from your revenue. Then, divide the gross profit by your revenue and multiply the result by 100 to express it as a percentage.
For example, if your gross profit is $40,000, and your revenue is $100,000:
Gross Profit Margin = ($40,000 / $100,000) x 100 = 40%
Calculating and monitoring gross profit margin regularly can help you assess your business’s financial health and identify areas for improvement.
Interpreting Gross Profit Margin
Interpreting your gross profit margin is crucial for understanding your business’s performance. A few key points to consider when analyzing this metric include:
- Higher Margin Indicates Efficiency: A higher gross profit margin typically suggests that your business is effectively managing its production or acquisition costs in relation to its revenue.
- Industry Comparisons: To gain more meaningful insights, compare your gross profit margin with industry benchmarks. This can help you assess how well you stack up against competitors.
- Trends Over Time: Monitoring your gross profit margin over time can reveal trends and potential issues. A declining margin may signal rising production costs or the need for pricing adjustments.
Importance of Gross Profit Margin in Financial Analysis
Gross profit margin plays a pivotal role in financial analysis for several reasons:
- Profitability Assessment: It helps you gauge the profitability of your core business operations, as it focuses solely on direct production costs.
- Decision-Making Tool: It aids in making informed decisions about pricing strategies, cost control measures, and overall business performance.
- Investor and Lender Confidence: Investors and lenders often scrutinize gross profit margin to assess the financial health and sustainability of a business.
In summary, gross profit margin is a critical metric for evaluating your business’s profitability and efficiency. By understanding how to calculate it, interpreting the results, and recognizing its importance in financial analysis, you can make data-driven decisions to enhance your company’s financial performance.
Factors Influencing Gross Profit
Understanding the factors that influence gross profit is essential for managing your business’s financial performance effectively.
Pricing Strategy
Your pricing strategy is a critical determinant of your gross profit. The prices you set for your products or services can have a significant impact on both your revenue and your profit margins. Here’s how pricing strategy can influence your gross profit:
- Competitive Pricing: Setting prices in line with or slightly above your competitors can help maximize sales volume but may lead to thinner profit margins.
- Premium Pricing: Charging higher prices for unique or high-quality products can result in higher profit margins, but it may also limit sales volume.
- Discount Strategies: Offering discounts can boost sales but may reduce your gross profit margin unless it leads to a significant increase in volume.
- Dynamic Pricing: Adjusting prices based on demand, seasonality, or other factors can optimize both revenue and profit margins.
A well-considered pricing strategy can strike the right balance between revenue and profit, aligning with your business goals.
Cost Control
Efficient cost control and management of the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) are fundamental to maintaining healthy gross profit margins. Strategies for controlling costs include:
- Supplier Negotiations: Negotiating favorable terms with suppliers, bulk purchasing, and securing discounts can lower your COGS.
- Inventory Management: Efficiently managing your inventory to minimize waste, spoilage, or obsolescence can reduce costs.
- Process Optimization: Streamlining production processes, improving productivity, and reducing waste can lower production costs.
- Technology Investments: Implementing technology solutions, such as inventory tracking software or automation, can enhance cost control.
Effective cost control ensures that a larger proportion of your revenue contributes to gross profit.
Sales Volume
The volume of goods or services you sell directly impacts your gross profit. The relationship between sales volume and gross profit can be summarized as follows:
- Increasing Sales Volume: While maintaining prices and costs, increasing sales volume can boost gross profit.
- Declining Sales Volume: A decrease in sales volume can put pressure on your profitability unless you adjust prices or reduce costs accordingly.
Striking the right balance between price, cost, and sales volume is crucial for optimizing gross profit.
Economic Factors
External economic factors can influence your business’s gross profit in various ways:
- Inflation: Rising prices of raw materials or labor can increase your COGS, potentially squeezing your profit margins.
- Currency Exchange Rates: If your business deals with international suppliers or customers, fluctuations in currency exchange rates can impact your costs and revenue.
- Consumer Demand: Economic downturns can affect consumer spending habits, directly impacting your sales volume and revenue.
- Market Competition: Increased competition can put pressure on prices and profit margins.
Monitoring and adapting to economic factors is essential for maintaining financial stability.
Industry-specific Considerations
Different industries have unique factors that can influence gross profit. These considerations can include:
- Regulations: Compliance with industry-specific regulations may add costs or limit pricing flexibility.
- Seasonality: Seasonal businesses may experience fluctuations in revenue and profit.
- Technological Advancements: Industries with rapid technological advancements may require ongoing investments to stay competitive.
Understanding and accounting for industry-specific factors is vital for effective gross profit management.
By considering and managing these factors, you can optimize your business’s gross profit, ensuring sustainable profitability and financial stability.
How to Improve Gross Profit?
Effectively managing and improving gross profit is essential for long-term business success. We’ll explore various strategies and tactics to enhance your gross profit margin.
How to Increase Gross Profit?
Boosting your gross profit involves implementing strategic measures that can lead to higher revenues or reduced costs. Here are some effective strategies to consider:
- Product Diversification: Expanding your product or service offerings can open new revenue streams and increase overall sales.
- Cross-Selling and Upselling: Encourage customers to purchase complementary or higher-margin products to maximize each transaction’s value.
- Targeted Pricing Increases: Identify products or services with price elasticity and consider modest price hikes to increase overall revenue.
- Quality Improvement: Enhance the quality or features of your offerings to justify higher prices, potentially improving gross profit margins.
- Market Expansion: Explore new markets or demographics to broaden your customer base and drive sales growth.
How to Reduce COGS?
Reducing the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) is a direct way to improve your gross profit margin. Consider the following cost-cutting strategies:
- Supplier Negotiations: Renegotiate terms with suppliers to secure better prices, discounts, or favorable payment terms.
- Efficient Procurement: Optimize your procurement processes to minimize waste, excess inventory, and unnecessary expenses.
- Streamlined Production: Improve production efficiency by eliminating bottlenecks, reducing downtime, and optimizing workflows.
- Outsourcing: Evaluate the feasibility of outsourcing certain aspects of production or services to reduce in-house costs.
- Quality Control: Implement stringent quality control measures to minimize defects and waste.
Pricing Optimization
Optimizing your pricing strategy is a delicate balancing act between maximizing revenue and maintaining profitability. Consider the following pricing strategies:
- Value-Based Pricing: Align your prices with the perceived value your product or service offers to customers.
- Dynamic Pricing: Adjust prices in real-time based on demand, inventory levels, or other factors to maximize profit.
- Bundling: Package related products or services together to encourage customers to purchase more and increase overall revenue.
- Tiered Pricing: Offer different pricing tiers with varying features or benefits to cater to a broader range of customers.
- Subscription Models: Implement subscription-based pricing to secure recurring revenue streams.
Sales and Marketing Tactics
Effective sales and marketing tactics can drive revenue growth without significantly increasing costs. Here are some tactics to consider:
- Targeted Advertising: Use data and analytics to focus your advertising efforts on the most lucrative customer segments.
- Customer Retention: Implement loyalty programs and customer retention strategies to boost repeat business.
- Digital Marketing: Leverage digital channels, such as social media and email marketing, to reach a broader audience cost-effectively.
- Sales Training: Invest in training and development for your sales team to improve their effectiveness in closing deals.
- Conversion Rate Optimization: Continuously optimize your sales funnel to increase the percentage of leads that convert into paying customers.
Examples of Gross Profit
To better understand the practical implications of gross profit, let’s explore some real-world examples and calculations. These examples will illustrate how gross profit can vary across different scenarios and industries.
Example 1: Retail Business
Imagine you own a small retail store that sells clothing. In a given month, your store generated $50,000 in revenue by selling various clothing items. To calculate your gross profit, you need to deduct the cost of the goods sold (COGS).
Calculation:
- Revenue: $50,000
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): $30,000
Gross Profit = Revenue – COGS = $50,000 – $30,000 = $20,000
In this example, your retail store’s gross profit for the month is $20,000. This means that after covering the direct costs associated with purchasing or manufacturing the clothing items you sold, you have $20,000 left to cover operating expenses and generate profit.
Example 2: Manufacturing Company
Suppose you run a manufacturing company that produces custom furniture. Over a year, your company generated $2,000,000 in revenue from furniture sales. However, your COGS includes expenses related to raw materials, labor, and production equipment.
Calculation:
- Revenue: $2,000,000
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): $1,200,000
Gross Profit = Revenue – COGS = $2,000,000 – $1,200,000 = $800,000
In this manufacturing example, your company’s gross profit for the year is $800,000. This amount represents the profit generated after accounting for the direct costs associated with producing the custom furniture.
Example 3: Service-Based Business
Consider a service-based business, such as a digital marketing agency. Over a quarter, the agency earned $100,000 in revenue by providing various marketing services to clients. The COGS for this type of business may include salaries of marketing specialists and software subscriptions.
Calculation:
- Revenue: $100,000
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): $40,000
Gross Profit = Revenue – COGS = $100,000 – $40,000 = $60,000
In this service-based business example, the agency’s gross profit for the quarter is $60,000. This represents the profit generated from providing services after deducting the direct costs associated with delivering those services.
These examples illustrate how gross profit calculations can vary depending on your business’s nature and industry. By understanding your gross profit, you can make informed decisions about pricing, cost management, and overall financial performance. It serves as a valuable tool for assessing profitability and guiding your business toward increased success.
Gross Profit vs. Net Profit
Understanding the distinction between gross profit and net profit is crucial for gaining deeper insights into your business’s financial performance.
Definition of Net Profit
Net Profit, often referred to as the bottom line or net income, represents the total profit your business earns after deducting all operating expenses, interest, taxes, and other non-operating costs from your gross profit. It’s the ultimate measure of your business’s profitability.
To calculate net profit, you start with your gross profit and then subtract:
- Operating Expenses: These include costs such as salaries, rent, utilities, marketing expenses, and administrative costs.
- Interest Expenses: Any interest paid on loans or credit lines used for business operations.
- Taxes: Income taxes, which vary depending on your business’s structure and location.
- Other Non-operating Costs: These can include one-time expenses, legal fees, or any extraordinary items that are not part of regular business operations.
Key Differences Between Gross Profit and Net Profit
While both gross profit and net profit are crucial financial metrics, they serve different purposes and capture distinct aspects of your business’s financial performance. Here are the key differences:
- Scope: Gross profit focuses exclusively on the direct costs of producing goods or services, whereas net profit accounts for all operating and non-operating expenses.
- Profitability Level: Gross profit measures profitability at the gross or production level, while net profit reflects overall business profitability after all expenses.
- Income Taxes: Gross profit doesn’t consider income taxes, whereas net profit accounts for taxes, which can significantly impact the final figure.
- Investor and Lender Perspective: Investors and lenders often look at both metrics, as they provide different insights into the business’s financial health.
Relationship Between Gross Profit and Net Profit
Gross profit serves as an intermediate step in the financial statement, leading to the calculation of net profit. The relationship between these two metrics can be expressed as follows:
Net Profit = Gross Profit – Operating Expenses – Interest Expenses – Taxes – Other Non-operating Costs
Understanding this relationship helps you grasp how gross profit contributes to the ultimate measure of your business’s profitability, net profit. While gross profit reflects the core profitability of your products or services, net profit takes into account the broader financial picture, including the impact of operating and non-operating expenses.
Common Misconceptions About Gross Profit
Misconceptions about gross profit are common, and they can lead to misunderstandings about your business’s financial health.
Debunking Myths and Misunderstandings
- Gross Profit Equals Net Profit: One of the most prevalent misconceptions is that gross profit is equal to net profit. As we’ve discussed, gross profit represents only the direct production costs, while net profit considers all expenses, including operating and non-operating costs.
- Gross Profit Margin Is the Only Indicator of Success: While a healthy gross profit margin is important, it’s not the sole indicator of business success. A high gross profit margin must be balanced with effective cost management and other financial factors for overall success.
Clarifying Gross Profit Concepts
- Gross Profit’s Role in Financial Analysis: Gross profit is a critical metric in assessing your business’s operational efficiency and profitability at the production level. It provides insights into how effectively you manage your direct costs.
- Complementary Metrics: While gross profit is important, it should be analyzed in conjunction with net profit, cash flow, and other financial metrics to provide a comprehensive view of your business’s financial performance.
By dispelling misconceptions and gaining a clear understanding of the relationship between gross profit and net profit, you can make more informed financial decisions and navigate your business towards greater profitability and financial success.
Conclusion
Gross profit is the cornerstone of financial success in any business. It represents the core profit generated from your primary operations, and understanding it is crucial for making informed decisions about pricing, cost management, and profitability. By mastering the concept of gross profit and its applications, you have taken a significant step toward achieving financial stability and growth in your business journey.
Remember, while gross profit is essential, it’s just one piece of the financial puzzle. To complete the picture, consider factors like net profit, cash flow, and strategic planning. Continuously monitor and optimize your gross profit to ensure that your business remains on a path to sustainable success.