- What are Financial Models?
- Why are Financial Models Important?
- Basic Financial Models
- Valuation Models
- Forecasting Models
- Risk Management Models
- Portfolio Optimization Models
- Financial Planning Models
- Sensitivity Analysis Models
- Industry-Specific Models
- Financial Modeling Software and Tools
- Best Practices for Financial Modeling
- Conclusion
Financial models play a crucial role in various aspects of finance, providing valuable insights for decision-making, forecasting, valuation, risk management, and more. Whether you’re an aspiring finance professional, an entrepreneur, or an investor, understanding different types of financial models is essential to make informed and strategic decisions.
In this guide, we will explore various types of financial models, their significance, and how they can be applied in different scenarios.
What are Financial Models?
Financial models are quantitative representations of real-world financial situations or scenarios. They are constructed using mathematical formulas, algorithms, and assumptions to simulate and analyze financial data. These models provide a structured framework for understanding and evaluating financial information, making projections, and supporting decision-making processes.
Why are Financial Models Important?
The importance of financial models lies in their ability to:
- Inform Decision-Making: Financial models provide valuable insights into the potential outcomes and implications of different financial decisions. They help individuals and organizations assess the impact of various factors and make informed choices that align with their goals and objectives.
- Assess Financial Performance: By analyzing historical data and projecting future scenarios, financial models allow for the evaluation of a company’s financial performance. They enable stakeholders to identify trends, strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement, aiding in strategic planning and risk management.
- Facilitate Forecasting and Planning: Financial models are instrumental in forecasting future financial outcomes. They help individuals and businesses estimate revenues, expenses, cash flows, and profitability. These forecasts are vital for budgeting, resource allocation, and setting realistic financial goals.
- Support Valuation and Investment Decisions: Valuation models, a subset of financial models, are crucial for assessing the value of assets, companies, or investment opportunities. They provide frameworks to determine fair prices, potential returns, and risks associated with investments, facilitating better investment decisions.
- Manage Risk: Financial models assist in identifying and managing financial risks. Through risk management models, individuals and organizations can quantify and evaluate potential risks, assess their impact, and implement strategies to mitigate them. This allows for more effective risk management and a reduction in potential financial losses.
- Optimize Portfolio Allocation: Portfolio optimization models aid in constructing investment portfolios that balance risk and reward. These models help investors diversify their holdings, allocate assets based on risk tolerance, and optimize returns. By using these models, investors can make strategic investment decisions aligned with their risk preferences and financial goals.
Basic Financial Models
Financial models serve as the foundation for analyzing and understanding a company’s financial performance. Mastering basic financial models provides a solid framework for more advanced analysis. Let’s explore the key types of basic financial models:
1. Income Statement Model
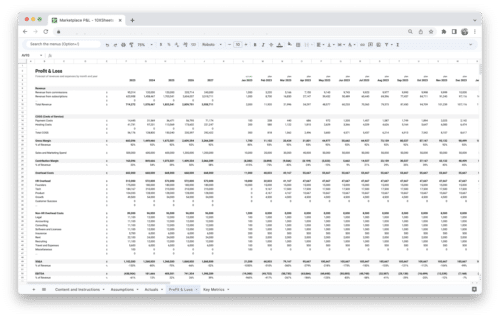
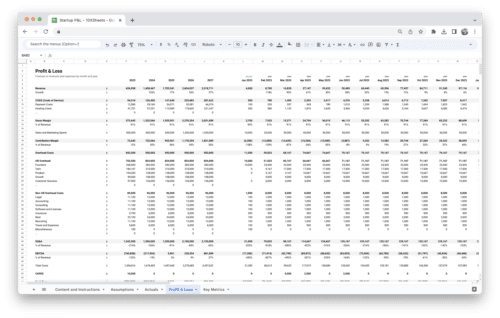
- An income statement model, also known as a profit and loss (P&L) model, helps assess a company’s revenue, expenses, and profitability over a specific period.
- Key components include revenue streams, cost of goods sold (COGS), operating expenses, taxes, and net income.
- By analyzing the income statement, you can gain insights into a company’s revenue drivers, cost structure, and overall financial health.
2. Balance Sheet Model
- A balance sheet model provides a snapshot of a company’s financial position at a given point in time.
- It includes assets (both current and long-term), liabilities, and shareholders’ equity.
- Understanding the balance sheet helps evaluate a company’s liquidity, solvency, and net worth.
3. Cash Flow Model
- A cash flow model tracks the inflow and outflow of cash within a company during a specific period.
- It includes operating cash flow, investing cash flow, and financing cash flow.
- Analyzing cash flow enables you to assess a company’s ability to generate cash, meet its financial obligations, and invest in future growth.
Valuation Models
Valuation models are used to estimate the intrinsic value of an asset or company. They are essential for investors, mergers and acquisitions, and determining fair value. Let’s delve into the three key types of valuation models:
1. Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) Model
- DCF is a widely used valuation model that estimates the present value of future cash flows.
- It considers the time value of money and calculates the net present value (NPV) by discounting projected cash flows at an appropriate discount rate.
- DCF helps determine the intrinsic value of an investment by assessing its potential profitability.
2. Comparable Company Analysis (CCA) Model
- CCA involves comparing the financial metrics and valuation multiples of similar companies within the same industry.
- It helps estimate the value of a company by benchmarking it against comparable public companies.
- By analyzing key financial ratios and metrics, such as price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio and enterprise value-to-EBITDA (EV/EBITDA) ratio, you can determine the relative valuation of a company.
3. Precedent Transaction Analysis (PTA) Model
- PTA involves analyzing past transactions involving similar companies to derive valuation benchmarks.
- It helps determine the value of a company by examining the pricing multiples paid in previous acquisitions or mergers.
- PTA provides insights into the valuation expectations and potential pricing for a company in a similar transaction.
Forecasting Models
Forecasting models enable financial professionals to predict future outcomes, which is crucial for planning, budgeting, and decision-making. Let’s explore the three key types of forecasting models:
1. Time Series Forecasting Models
- Time series forecasting models analyze historical data to predict future values based on patterns and trends.
- Techniques such as moving averages, exponential smoothing, and ARIMA (autoregressive integrated moving average) are commonly used.
- Time series forecasting assists in predicting sales, demand, stock prices, and other time-dependent variables.
2. Regression-Based Forecasting Models
- Regression analysis identifies relationships between variables to predict future outcomes.
- It involves analyzing historical data and using statistical techniques to estimate the impact of independent variables on the dependent variable.
- Regression-based models are useful for forecasting sales, market demand, and other scenarios with multiple influencing factors.
3. Scenario-Based Forecasting Models
- Scenario-based forecasting models explore different hypothetical scenarios to assess their impact on financial outcomes.
- By creating best-case, worst-case, and moderate-case scenarios, you can evaluate potential risks and opportunities.
- Scenario-based models are beneficial in strategic planning, risk assessment, and sensitivity analysis.
Risk Management Models
Risk management models help identify, assess, and mitigate financial risks. They are crucial for businesses and investors to minimize potential losses. Let’s examine the three key types of risk management models:
1. Value at Risk (VaR) Model
- VaR estimates the maximum potential loss within a specific confidence level over a given time horizon.
- It combines historical data, statistical analysis, and market factors to quantify the risk exposure.
- VaR is widely used in portfolio management and risk assessment.
2. Monte Carlo Simulation Model
- Monte Carlo simulation models utilize random sampling techniques to simulate a range of possible outcomes.
- It incorporates multiple variables and their probability distributions to assess the impact of uncertainty on financial models.
- Monte Carlo simulation is useful in risk analysis, option pricing, and project evaluation.
3. Credit Risk Models
- Credit risk models assess the probability of default and estimate potential losses in credit portfolios.
- They utilize financial ratios, credit scores, historical data, and statistical techniques to evaluate creditworthiness.
- Credit risk models help financial institutions and lenders make informed lending decisions.
Portfolio Optimization Models
Portfolio optimization models aid in constructing investment portfolios to maximize returns while managing risk. They play a crucial role in asset allocation and diversification. Let’s explore the three key types of portfolio optimization models:
1. Markowitz Mean-Variance Model
- The Markowitz model combines expected returns and risk (variance or standard deviation) to find an optimal portfolio.
- It helps identify the ideal asset allocation that balances risk and reward based on investors’ risk tolerance.
- The Markowitz model is widely used in modern portfolio theory.
2. Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM)
- CAPM estimates the expected return on an investment by considering its systematic risk.
- It factors in the risk-free rate, market risk premium, and beta coefficient to determine the required return.
- CAPM is frequently employed in pricing and valuing securities.
3. Black-Litterman Model
- The Black-Litterman model combines investors’ views with market equilibrium to enhance portfolio optimization.
- It integrates subjective views on expected returns with the market consensus to arrive at an optimal portfolio allocation.
- The Black-Litterman model is useful when investors have unique insights or beliefs about asset performance.
Financial Planning Models
Financial planning models facilitate personal and business financial decision-making by forecasting future scenarios and evaluating various options. Let’s explore the three key types of financial planning models:
1. Budgeting Models
- Budgeting models help individuals and organizations allocate resources and plan expenses.
- They provide a framework for setting financial goals, estimating income, and managing expenditures.
- Budgeting models assist in tracking financial performance and making adjustments as needed.
2. Retirement Planning Models
- Retirement planning models help individuals estimate their future financial needs during retirement.
- They consider factors such as income, expenses, savings, investments, and retirement age to determine the required retirement fund.
- Retirement planning models guide individuals in making contributions, investments, and savings decisions.
3. Capital Expenditure Planning Models
- Capital expenditure planning models assist businesses in evaluating potential investments in assets or projects.
- They consider factors such as cash flows, payback period, return on investment (ROI), and net present value (NPV).
- Capital expenditure planning models support decision-making by quantifying the financial impact of investments.
Sensitivity Analysis Models
Sensitivity analysis models evaluate the impact of changes in variables or assumptions on financial outcomes. They assist in assessing the robustness and sensitivity of financial models. Let’s explore the three key types of sensitivity analysis models:
1. One-Way Sensitivity Analysis
- One-way sensitivity analysis examines the effect of varying one variable while keeping others constant.
- It helps identify the most influential factors and their impact on financial outcomes.
- One-way sensitivity analysis provides insights into the sensitivity of the model to specific variables.
2. Two-Way Sensitivity Analysis
- Two-way sensitivity analysis explores the simultaneous variations of two variables to assess their combined impact.
- It helps understand the interaction and interdependence between variables and their effects on outcomes.
- Two-way sensitivity analysis provides a comprehensive understanding of the model’s sensitivity.
3. Monte Carlo Sensitivity Analysis
- Monte Carlo sensitivity analysis involves running multiple simulations by varying multiple variables simultaneously.
- It provides a distribution of possible outcomes and their probabilities based on random sampling techniques.
- Monte Carlo sensitivity analysis offers a robust assessment of the model’s sensitivity to multiple variables.
Industry-Specific Models
Different industries often require specialized financial models tailored to their unique characteristics and requirements. Let’s explore some examples of industry-specific financial models:
1. Real Estate Investment Models
- Real estate investment models assist in evaluating the financial feasibility of property investments.
- They consider factors such as property value, rental income, expenses, financing, and projected returns.
- Real estate investment models help investors make informed decisions about buying, selling, or developing properties.
2. Banking and Financial Services Models
- Banking and financial services models encompass various models used in financial institutions.
- Examples include credit risk models, loan pricing models, liquidity models, and interest rate models.
- These models support risk management, pricing, profitability analysis, and regulatory compliance.
3. Manufacturing and Supply Chain Models
- Manufacturing and supply chain models assist in optimizing production, inventory management, and logistics.
- They include models such as production planning models, demand forecasting models, and inventory optimization models.
- Manufacturing and supply chain models help businesses enhance operational efficiency and minimize costs.
Financial Modeling Software and Tools
To effectively build and analyze financial models, utilizing appropriate software and tools is crucial. Let’s explore some popular options:
1. Excel
- Excel is widely used for financial modeling due to its versatility and extensive features.
- It allows for building complex financial models with formulas, functions, data manipulation, and charting capabilities.
- Excel is commonly used for basic to advanced financial analysis and modeling.
2. Dedicated Financial Modeling Software
- Dedicated financial modeling software, such as Bloomberg Terminal, FactSet, and MATLAB, offers specialized features for financial modeling.
- These software solutions provide access to extensive financial data, advanced modeling capabilities, and industry-specific tools.
- Dedicated financial modeling software is commonly used in professional finance settings.
3. Online Financial Modeling Platforms
- Online financial modeling platforms, like Vena Solutions, Databox, and PlanGuru, provide cloud-based solutions for collaborative modeling and analysis.
- These platforms offer features such as data integration, scenario analysis, version control, and sharing capabilities.
- Online financial modeling platforms are suitable for team collaboration and remote work scenarios.
Best Practices for Financial Modeling
To ensure accuracy, reliability, and effectiveness in financial modeling, it’s essential to follow best practices. Here are some key tips:
- Clearly define the objectives and scope of the financial model before starting.
- Use consistent and reliable data from reputable sources.
- Organize the model structure logically and maintain proper documentation.
- Implement error-checking mechanisms and perform regular model audits.
- Validate the model’s outputs against real-world data and historical performance.
- Test different scenarios and assumptions to assess the model’s sensitivity.
- Keep the model flexible and adaptable to accommodate changing variables and conditions.
- Regularly update and review the financial model to reflect the latest information and assumptions.
- Seek feedback and input from subject-matter experts to improve the model’s accuracy and relevance.
Conclusion
Financial modeling is a vital skill for finance professionals, entrepreneurs, and investors alike. Understanding various types of financial models equips you with the tools to analyze data, make informed decisions, and navigate complex financial landscapes. By mastering basic financial models, valuation models, forecasting models, risk management models, portfolio optimization models, and industry-specific models, you can enhance your financial acumen and drive better outcomes. Continuously learning, practicing, and staying updated with best practices will empower you to excel in financial modeling and thrive in the dynamic world of finance.
Get Started With a Prebuilt Template!
Looking to streamline your business financial modeling process with a prebuilt customizable template? Say goodbye to the hassle of building a financial model from scratch and get started right away with one of our premium templates.
- Save time with no need to create a financial model from scratch.
- Reduce errors with prebuilt formulas and calculations.
- Customize to your needs by adding/deleting sections and adjusting formulas.
- Automatically calculate key metrics for valuable insights.
- Make informed decisions about your strategy and goals with a clear picture of your business performance and financial health.