- Foundations of Revenue Forecasting
- How to Do Revenue Forecasting?
- Qualitative Revenue Forecasting Methods
- Quantitative Revenue Forecasting Methods
- Implementing Revenue Forecasting Techniques
- Validating and Refining Revenue Forecasts
- Incorporating External Factors in Revenue Forecasting
- Monitoring and Updating Revenue Forecasts
- Revenue Forecasting Best Practices
- Revenue Forecasting Challenges and Limitations
- Conclusion
Revenue forecasting is a critical aspect of business planning, enabling organizations to accurately predict and project their future revenue streams. By implementing effective revenue forecasting techniques, businesses can make informed decisions, allocate resources efficiently, and set realistic financial goals.
In this guide, we will explore the foundations, methods, and best practices of revenue forecasting, equipping you with the knowledge and tools to develop accurate revenue forecasts for your business.
Foundations of Revenue Forecasting
Revenue Forecasting Key Concepts and Terminologies
Revenue forecasting involves several key concepts and terminologies that provide the foundation for understanding and implementing accurate forecasts. These include:
- Revenue: The income generated from the sale of goods or services.
- Forecasting: The process of estimating future revenue based on historical data, market trends, and other relevant factors.
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Metrics used to evaluate and measure the performance and success of revenue forecasting.
- Time Series Analysis: A statistical technique used to analyze patterns and trends in historical revenue data.
Types of Revenue Forecasting Models
Revenue forecasting models can be broadly classified into qualitative and quantitative models.
- Qualitative Forecasting: Relies on expert opinions, market research, and subjective judgments to predict future revenue.
- Quantitative Forecasting: Utilizes historical data and statistical methods to generate revenue forecasts.
Factors Affecting Revenue Forecasting
Various internal and external factors influence revenue forecasting. It is crucial to consider these factors when developing forecasts. Some key factors include:
- Market Demand and Trends: Changes in customer preferences, market conditions, and industry dynamics can impact revenue.
- Economic Conditions: Fluctuations in the economy, such as GDP growth, inflation rates, and interest rates, can influence consumer spending and revenue.
- Competitive Landscape: The activities of competitors, market share, and pricing strategies can affect revenue forecasts.
- Seasonality: Many businesses experience seasonal variations in revenue, which must be considered for accurate forecasting.
- Product Lifecycle: The stage of a product’s lifecycle, including introduction, growth, maturity, and decline, affects revenue projections.
Relationship between Revenue Forecasting and Financial Planning
Revenue forecasting is closely intertwined with financial planning. Accurate revenue forecasts serve as a basis for developing budgets, setting sales targets, and formulating financial strategies. By aligning revenue forecasts with financial planning, businesses can ensure realistic and achievable financial goals.
How to Do Revenue Forecasting?
1. Defining Forecasting Goals and Objectives
Before embarking on revenue forecasting, defining clear goals and objectives is essential. This involves determining the purpose of the forecast, such as budgeting, resource allocation, or strategic planning. Clearly defined goals provide focus and guide the entire forecasting process.
2. Gathering Historical Revenue Data
Historical revenue data serves as the foundation for accurate forecasting. Collect and analyze revenue data for previous periods, considering factors such as sales volume, revenue by product or service, customer segments, and geographic regions. Ensure the data is reliable, consistent, and covers a sufficient time frame to capture trends and patterns.
3. Identifying Relevant Metrics and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
To develop meaningful revenue forecasts, it is crucial to identify the key metrics and KPIs that align with your business goals. Some common revenue-related metrics include:
- Total Revenue
- Revenue Growth Rate
- Average Revenue per Customer
- Revenue by Product or Service Category
- Revenue by Customer Segment
4. Cleaning, Organizing, and Validating Data
Before analyzing historical revenue data, it is essential to clean, organize, and validate the data. This includes:
- Removing outliers and inconsistencies
- Standardizing data formats
- Resolving missing or incomplete data
- Ensuring data accuracy and integrity
5. Establishing Assumptions and Constraints
Revenue forecasting requires making assumptions and setting constraints to ensure realistic and achievable forecasts. When establishing assumptions and limitations, consider factors such as market conditions, pricing changes, industry trends, and internal capabilities.
Qualitative Revenue Forecasting Methods
Expert Opinion and Market Research
Expert opinions and market research can provide valuable insights into future revenue trends. This qualitative approach involves gathering input from industry experts, market analysts, and internal stakeholders to understand market dynamics and potential revenue drivers.
Delphi Method
The Delphi method is a structured approach to gathering and consolidating expert opinions. It involves multiple rounds of anonymous surveys or interviews, with experts revising their forecasts based on collective feedback. This iterative process helps to converge toward a more accurate revenue forecast.
Customer Surveys and Feedback Analysis
Engaging with customers through surveys and analyzing their feedback can provide valuable information for revenue forecasting. Customer surveys can gather insights into purchase intentions, preferences, and customer satisfaction, which can be used to project future revenue.
Case Studies and Analogous Forecasting
Analyzing case studies and analogous industries or companies can provide a useful reference point for revenue forecasting. By studying similar businesses or markets and understanding their revenue patterns, you can make informed estimates for your own forecasts.
Quantitative Revenue Forecasting Methods
Time Series Analysis
Time series analysis utilizes historical revenue data to identify patterns, trends, and seasonality, allowing for the projection of future revenue. This quantitative method includes the following steps:
- Moving Averages: Calculate moving averages to smooth out fluctuations and identify underlying trends in revenue data.
- Exponential Smoothing: Assign weights to historical data, giving more weight to recent periods, and use this weighted average to generate future revenue projections.
- Trend Analysis: Identify long-term upward or downward trends in revenue data and extrapolate them to forecast future revenue.
- Seasonality and Cyclical Adjustments: Identify seasonal patterns and cyclical fluctuations in revenue, and apply appropriate adjustments to forecast future revenue accurately.
Regression Analysis
Regression analysis helps establish relationships between revenue and other relevant variables, allowing for more accurate revenue forecasts. This quantitative method includes:
- Simple Linear Regression: Analyze the relationship between revenue and a single predictor variable (e.g., advertising expenditure) to develop a linear regression model for forecasting.
- Multiple Regression: Consider various predictor variables (e.g., advertising expenditure, market share, and GDP growth) to build a regression model that incorporates numerous factors affecting revenue.
Market Segmentation
Market segmentation involves dividing the target market into distinct customer segments based on shared characteristics and behavior. This method includes:
- Identifying Customer Segments: Segment the market based on demographics, geographic location, psychographics, or other relevant criteria to define customer groups.
- Analyzing Customer Behavior and Patterns: Analyze historical revenue data for each customer segment to identify trends, preferences, and purchasing patterns.
- Projecting Revenue by Segment: Develop revenue forecasts for each customer segment, considering factors specific to each segment, such as growth rates, market share, and market trends.
Econometric Models
Econometric models utilize statistical techniques to estimate the relationship between revenue and various economic variables. This includes:
- Building and Validating Models: Select relevant economic indicators (e.g., GDP, interest rates) and build econometric models that capture their impact on revenue. Validate these models using historical data.
- Interpreting Results and Forecasts: Analyze the results of econometric models to understand the magnitude and significance of the relationship between revenue and economic variables. Use these insights to generate revenue forecasts based on economic forecasts.
Implementing Revenue Forecasting Techniques
Excel and Spreadsheet Applications
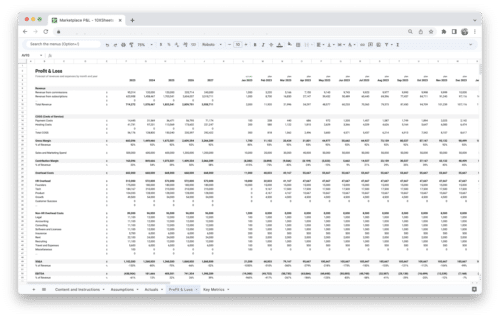
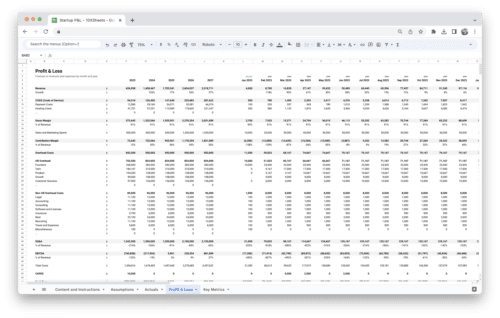
Excel and other spreadsheet applications provide a flexible and accessible platform for implementing revenue forecasting techniques. Utilize various functions, formulas, and data manipulation techniques to analyze historical data, generate forecasts, and create visualizations and graphs.
Forecasting Software and Tools
Numerous forecasting software and tools are available to streamline the revenue forecasting process. These tools offer advanced analytics capabilities, data visualization, and automation features. Consider factors such as ease of use, compatibility with existing systems, and specific forecasting requirements when selecting a tool.
Predictive Analytics and Machine Learning in Revenue Forecasting
Predictive analytics and machine learning techniques can enhance revenue forecasting accuracy by analyzing large volumes of data and identifying complex patterns. These advanced methods can uncover hidden insights and improve forecast precision.
Monte Carlo Simulation for Revenue Forecasting
Monte Carlo simulation is a powerful technique that uses random sampling to generate multiple scenarios and assess the range of possible revenue outcomes. Considering different combinations of input variables provides a probabilistic view of revenue forecasts, accounting for uncertainties and risks.
Validating and Refining Revenue Forecasts
Sensitivity Analysis
Sensitivity analysis involves assessing how changes in key input variables impact revenue forecasts. By varying assumptions and constraints, you can understand the sensitivity of forecasts and identify critical factors that significantly affect revenue outcomes.
Scenario Planning
Scenario planning entails creating multiple scenarios based on different assumptions, external factors, and market conditions. By developing best-case, worst-case, and moderate scenarios, you can assess the potential impact on revenue and evaluate the resilience of your business under different circumstances.
Assessing Forecast Accuracy
Evaluating forecast accuracy is essential to refine and improve revenue forecasts over time. Compare actual revenue data with forecasted values, calculate forecasting errors (e.g., mean absolute percentage error), and identify areas for improvement.
Adjusting and Fine-tuning Forecasts
Based on the sensitivity analysis results, scenario planning, and accuracy assessments, make necessary adjustments and fine-tune revenue forecasts. Incorporate new information, market feedback, and emerging trends to ensure forecasts reflect the most up-to-date insights.
Incorporating External Factors in Revenue Forecasting
Market Trends and Industry Analysis
Stay informed about market trends, industry developments, and emerging technologies that can impact revenue. Monitor competitors, customer preferences, and market dynamics to adjust forecasts accordingly.
Competitive Landscape and Benchmarking
Analyze the competitive landscape to understand how competitors’ actions and strategies may affect revenue. Benchmark your business against industry peers to identify areas of strength and opportunities for improvement.
Economic Indicators and Macroeconomic Factors
Keep an eye on economic indicators such as GDP growth, inflation rates, consumer confidence, and interest rates. Changes in the macroeconomic environment can significantly impact revenue and should be considered in forecasting.
Regulatory and Legal Considerations
Understand the regulatory landscape and legal requirements specific to your industry. Anticipate the potential impact of new regulations or changes in legislation on revenue streams and adjust forecasts accordingly.
Monitoring and Updating Revenue Forecasts
Establishing Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Define relevant KPIs to monitor and evaluate revenue performance against forecasts. Some common revenue-related KPIs include revenue growth rate, revenue by product or service category, customer lifetime value, and customer acquisition cost.
Tracking and Analyzing Actual Performance
Continuously track and analyze actual revenue performance against forecasts. Regularly review revenue data, compare with forecasted values, and identify any deviations or trends that may require adjustments to future forecasts.
Revising Forecasts Based on New Information
As new information becomes available, such as market research data, customer feedback, or changes in economic conditions, update revenue forecasts accordingly. Maintain flexibility and adaptability to refine forecasts as needed.
Communicating Forecast Updates to Stakeholders
Effective communication of forecast updates is crucial for aligning stakeholders and ensuring transparency. Share revised forecasts, explain the rationale behind adjustments, and provide insights on market conditions and external factors influencing revenue.
Revenue Forecasting Best Practices
To ensure effective revenue forecasting, here are some best practices to keep in mind:
- Data Integrity and Quality Control: Ensure data used for revenue forecasting is accurate, reliable, and consistent. Implement data quality control measures, regularly validate data integrity, and address any issues promptly.
- Collaboration and Cross-Functional Involvement: Foster collaboration between departments and involve key stakeholders in the forecasting process. Seek input from sales, marketing, finance, and operations teams to gather diverse perspectives and enhance forecast accuracy.
- Continuous Learning and Improvement: Revenue forecasting is an ongoing process that requires continuous learning and improvement. Stay updated on industry trends, new forecasting techniques, and emerging technologies to refine forecasting capabilities.
- Documenting and Communicating Forecasts: Document the assumptions, methodologies, and results of revenue forecasts. Maintain clear and transparent documentation to facilitate understanding, communication, and future reference.
Revenue Forecasting Challenges and Limitations
Revenue forecasting comes with its own set of challenges and limitations, including:
- Forecasting in Uncertain and Volatile Environments: Forecasting revenue accurately becomes more challenging in uncertain and volatile environments. Factors such as economic instability, market disruptions, or unexpected events can introduce higher levels of uncertainty into forecasts.
- Overcoming Data Limitations and Biases: Revenue forecasting relies on data availability and quality. Overcome data limitations and biases by incorporating external data sources, implementing data validation processes, and conducting sensitivity analysis to assess the impact of data uncertainties.
- Dealing with Forecasting Errors and Discrepancies: Despite best efforts, forecasting errors and discrepancies may occur. Develop strategies to promptly identify and address forecasting errors, such as adjusting models, reassessing assumptions, or refining data collection processes.
Conclusion
Implementing effective revenue forecasting techniques is crucial for organizations to make informed decisions, set realistic financial goals, and adapt to changing market conditions. Following the step-by-step approach outlined in this guide, you can develop accurate revenue forecasts that serve as a solid foundation for financial planning and strategic decision-making. Stay informed of industry trends, leverage advanced technologies, and continuously refine your forecasting processes to stay ahead in an ever-evolving business landscape.
Get Started With a Prebuilt Template!
Looking to streamline your business financial modeling process with a prebuilt customizable template? Say goodbye to the hassle of building a financial model from scratch and get started right away with one of our premium templates.
- Save time with no need to create a financial model from scratch.
- Reduce errors with prebuilt formulas and calculations.
- Customize to your needs by adding/deleting sections and adjusting formulas.
- Automatically calculate key metrics for valuable insights.
- Make informed decisions about your strategy and goals with a clear picture of your business performance and financial health.